OneMCP Architecture
This document provides a technical overview of the OneMCP runtime, describing how requests propagate through the system and how each subsystem interacts during planning, execution, and evaluation.
1. System Diagram
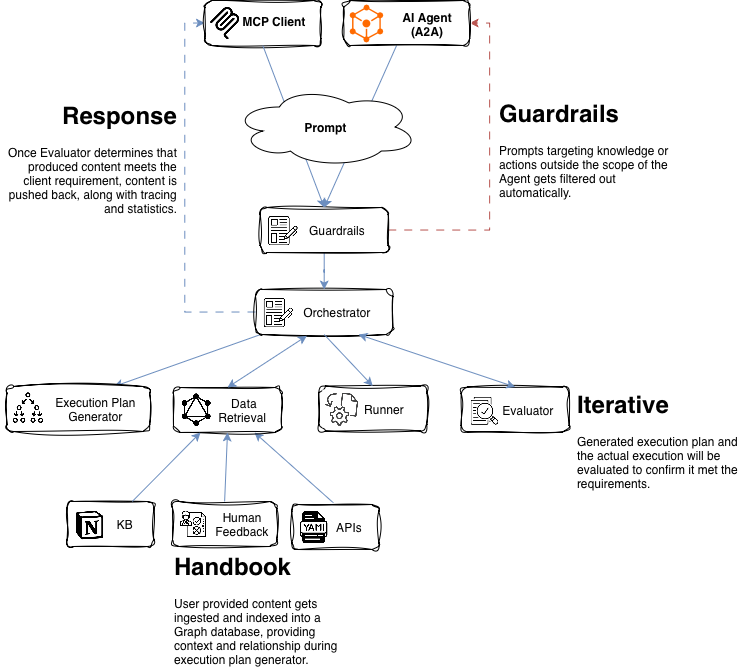
Use this diagram as the reference model for all sections below.
2. Core Components
Guardrails
A deterministic filtering layer that validates:
- Allowed actions
- Tool / API call permissions
- Domain constraints and policy restrictions
- Unsupported or unsafe operations
Guardrails run before orchestration and after execution to ensure all operations are grounded and safe.
Orchestrator
The orchestration engine responsible for:
- Taking the raw prompt assignment
- Selecting relevant Handbook context
- Generating an ordered execution plan
- Splitting work across the Runner, Data Retrieval, and Evaluator
Key behavior:
- Plans are generated deterministically from validated context
- Orchestrator re-queries Data Retrieval when context resolution is incomplete
- Loops execution + evaluation until plan completion or guardrail violation
Data Retrieval
The contextual lookup service backed by the Handbook graph.
Responsibilities:
- Returning minimal-but-sufficient context per assignment
- Semantic + structural lookup against Handbook nodes
- Providing execution-time references for API definitions, constraints, and docs
- Improving recall/precision through LLM-optimized embeddings (during indexing)
Outputs:
- Structured payloads (schemas, capabilities, constraints) consumed directly by the Orchestrator.
Handbook
Authoritative knowledge graph used to drive all grounded behavior.
Contains:
- Guardrails (constraint schemas, policies, domain rules)
- API Definitions (OpenAPI specs, generated client methods)
- Documentation (human-authored usage guides)
- Regression Tests (expected behaviors, edge-case validations)
- User Feedback (used to adjust future plan generation)
The Handbook is immutable during a request. Indexing/optimization happens offline.
Runner
Executes the generated execution plan with strict isolation.
Capabilities:
- Perform validated tool/API calls
- Maintain network connectivity to enterprise services
- Stream logs, intermediate results, and artifacts
- Support stepwise execution for inspection & debugging
The Runner does not own any planning logic; it simply performs actions created by the Orchestrator.
Evaluator
Post-execution validation engine.
Checks:
- Action outputs vs. expected schemas
- Adherence to Guardrails
- End-to-end consistency and correctness
- Plan-level vs. step-level validity
If evaluation fails, the Orchestrator receives error states and can:
- Regenerate sub-plans
- Request additional context
- Abort with actionable diagnostics
3. The Three Developer Pillars
1) Handbook = Ground Truth
All behavior must map to Handbook-backed capabilities.
Dev implications:
- Add new API? → Update Handbook API definitions
- Add new constraints? → Extend Guardrail nodes
- Add new behaviors? → Add documentation + regression tests
- Fix model misunderstandings? → Add user feedback entries
The Handbook determines what the agent can and cannot do.
2) Contextual Retrieval = Deterministic Context Boundary
Retrieval enforces scoped execution, reducing hallucination risk.
Developer responsibilities:
- Ensure new Handbook assets include correct metadata/tags
- Validate embeddings during indexing
- Use execution tracing to debug missing or noisy context
Tracing (per assignment) includes:
- Context selection
- Plan generation steps
- Execution transcript
- Evaluation results
This is essential when debugging incorrect agent behavior.
3) Runtime = Extract → Validate → Plan → Execute → Evaluate
This is the strict lifecycle for every request.
1. Extract
Identify relevant Handbook context for the assignment.
2. Validate
Reject prohibited or unsupported operations via Guardrails.
3. Plan
Produce an execution plan:
- Action sequence
- Tool/API call mapping
- Inputs + expected outputs
4. Execute
Runner performs every step with isolation + streaming.
5. Evaluate
Evaluator checks correctness and guardrail compliance.
If evaluation fails → Runtime loops back to planning with new constraints.
4. Developer Notes & Best Practices
Adding new capabilities
- Update Handbook documentation
- Add API specs + client stubs
- Add regression tests
- Define/extend guardrail logic
Debugging incorrect behavior
Use:
- Execution trace logs
- Context retrieval logs
- Plan generation trace
- Evaluation diagnostics
Improving retrieval quality
- Ensure Handbook items have consistent metadata
- Add examples or regression tests for ambiguous cases
- Refine domain-specific guardrails